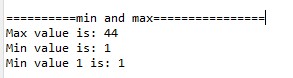Java 8 Streams – Streams in Java With Examples
What are Streams?
- Sequence of objects supporting multiple methods.
Features:
- Stream is not a data structure and does not store elements.
- Source of stream remains unmodified after operations are performed.
- Streams perform operation over the collection but actually does not modify the underlying collection.
- Laziness, evaluates only when requried. (When Terminal operation is identified)
- Visitation of elements only once, to revisit we need new stream. If same stream used it throws IllegalStateException.
Laziness:
- Intermediate operations are not evaluated until terminal operation invoked.
- Each intermediate operation creates a new stream and process and returns stream.
- When terminal invoked, traversal begins and operations are performed one by one.
- Parallel streams does not evaluate only by one but simultaneously based on available ones.
Intermediate and Terminal Operations:
- Every stream will perform Intermediate and Terminal Operations.
- There can be any number of Intermediate operations but only one Terminal operation
- Streams will not process until it reaches the Terminal operation, once it reaches Terminal operation then only stream processing will start.
- It is mandatory for a stream to have Terminal operation for the stream to process or Streams will not process.
| Intermediate Operations | Terminal Operations |
| filter | toArray() |
| map | Collect |
| flatmap | Count |
| distinct | reduce |
| sorted | forEach |
| limit | forEachOrdering |
| skip | min |
| peek | max |
| Anymatch | |
| allmatch | |
| nonematch | |
| findfirst | |
|
findany |
let us see some examples of some Intermediate and Terminal operations,
class Student {
String studentName;
List<String> studentSubjects;
int salary;
/**
* @return the salary
*/
public int getSalary() {
return salary;
}
/**
* @param salary the salary to set
*/
public void setSalary(int salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
public String getStudentName() {
return studentName;
}
public void setStudentName(String studentName) {
this.studentName = studentName;
}
public List<String> getStudentSubjects() {
return studentSubjects;
}
public void setStudentSubjects(List<String> studentSubjects) {
this.studentSubjects = studentSubjects;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [studentName=" + studentName + ", studentSubjects=" + studentSubjects + "]";
}
}
Let us create a main method to populate the object,
public class Operations {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> strList1 = Arrays.asList("Zebra","Alpha", "Beta", "Charlie", "Delta", "Alp", "Alphine", "Alphabet");
List<Integer> intList = Arrays.asList(10,35,44,32,1);
Student student1 = new Student();
student1.setStudentName("Alpha Student");
List<String> stud1Subj = new LinkedList<String>();
stud1Subj.add("Computers");
stud1Subj.add(" Information Technology");
student1.setStudentSubjects(stud1Subj);
student1.setSalary(10000);
Student student2 = new Student();
student2.setStudentName("Beta Student");
List<String> stud2Subj = new LinkedList<String>();
stud2Subj.add("Java");
stud2Subj.add(" Spring");
student2.setStudentSubjects(stud2Subj);
student2.setSalary(200000);
List<Student> studList = Arrays.asList(student1, student2);
System.out.println("==================== STUDLIST========================");
System.out.println(studList);
System.out.println();
}
}
Output:
==================== STUDLIST========================
[Student [studentName=Alpha Student, studentSubjects=[Computers, Information Technology]], Student [studentName=Beta Student, studentSubjects=[Java, Spring]]]
Map vs FlatMap:
Map produces one output value for each input value
FlatMap takes one input value and provides arbitrary number of values. In short helps to flatten a Collection<Collection<T>> into a Collection<T>.
Now let us see an example,
List<List<String>> mapList = studList.stream().map(Student::getStudentSubjects).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println("========== Map in Stream ==========");
mapList.forEach(System.out::print);
System.out.println();
List<String> flatmapList = studList.stream().map(Student::getStudentSubjects).flatMap(Collection::stream).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println("========== FlatMap in Stream ==========");
flatmapList.forEach(System.out::print);
Output:
Distinct:
To get unique values from the collection.
List<String> distincts = strList1.stream().distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println("========== Distinct ==========");
distincts.forEach(x -> System.out.print(x+" "));
System.out.println();
Output:
Limit:
Limit result to certain number of records. In the below example we are limiting the total number of records to 3.
List<String> limits = strList1.stream().limit(3).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println("========== LIMIT ==========");
limits.forEach(x -> System.out.print(x+" "));
System.out.println();
Peek:
When we have to view any value in the middle of Stream operations, We can use peek.
Set<String> peekValue = strList1.stream().filter(x -> x.equals("Alpha")).peek(s -> System.out.println(s)).collect(Collectors.toSet());
System.out.println("========== PEEK ==========");
peekValue.forEach(x -> System.out.print(x+" "));
System.out.println();
Output:
Skip:
Skips the specific number of elements. In the below example, first 3 elements are skipped and values are printed from 4th element.
List<String> skipList = strList1.stream().skip(3).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println("========== Skip ==========");
skipList.forEach(x -> System.out.print(x+" "));
System.out.println();
Sorting:
We can do sorting using Streams, reverse sorting and natural order sorting. We had done reverse and natural order sorting in the below example.
List<String> sorting = strList1.stream().sorted(Comparator.reverseOrder()).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println("========== Sorted Reverse ==========");
sorting.forEach(x -> System.out.print(x+" "));
System.out.println();
List<String> sorting1 = strList1.stream().sorted(Comparator.naturalOrder()).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println("========== Sorted Natural Order ==========");
sorting1.forEach(x -> System.out.print(x+" "));
System.out.println();
List<String> sorting2 = strList1.stream().sorted().collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println("========== SORTING ==========");
sorting2.forEach(x -> System.out.print(x+" "));
System.out.println();
Count:
To count the number to elements in the collection.
long num = strList1.stream().count();
System.out.println("========== Count ==========");
System.out.println(num);
System.out.println();
Min And Max:
To find the Minimum and Maximum from collection. Below are few examples,
System.out.println("==========min and max================");
int max = intList.stream().max(Integer::compare).get();
System.out.println("Max value is: "+max);
int min = intList.parallelStream().min(Integer::compare).get();
System.out.println("Min value is: "+min);
int min1 = intList.parallelStream().max(Comparator.reverseOrder()).get();
System.out.println("Min value 1 is: "+min1);
System.out.println();
ForEach vs Stream.forEach:
Both are used for Iterating a collection, The difference between them are,
forEach – Does not maintain order
Stream.forEach – Maintains Order
System.out.println("===========for each vs stream.foreach============");
strList1.forEach(s -> System.out.print(s+" "));
System.out.println();
strList1.parallelStream().forEach(s -> System.out.print(s+" "));
System.out.println();
Reduce:
Used to perform operations are multiple values and returns a single result. In the below example we have used addition.
int reduce = intList.parallelStream().reduce((x1,x2)-> x1+x2).get();
System.out.println("======= Reduce ===========");
System.out.println("Reduce is: "+reduce);
System.out.println();
Filter, FindAny, FindFirst, AnyMatch and AllMatch:
Filter: Similar to if condition to search or find any value
FindAny: Returns an object which may or may not contain a non-null value
FindFirst: Finds the first element when it is matched
AnyMatch: Return true if atleast one element matches the condition
AllMatch: Returns true if all elements in the stream are matched (satisfies the condition)
//Filter operation
System.out.println("======= Filter ===========");
Optional<String> filterValue = strList1.parallelStream().filter(x -> x.equalsIgnoreCase("delta")).findFirst();
System.out.println("Filter with findfirst: "+filterValue);
System.out.println();
//Stream with Filter
String filterContains = strList1.stream().filter(s -> s.equalsIgnoreCase("charlie")).findAny().get();
System.out.println("Filter with findAny: "+filterContains);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("======= Find Any ===========");
boolean findAny = strList1.stream().filter(s -> s.equalsIgnoreCase("che")).findAny().isPresent();
System.out.println("FindAny isPresent: "+findAny);
System.out.println();
String findAnyTest = strList1.stream().filter(s -> s.contains("Alp")).findAny().get();
System.out.println("Find Any with value: "+findAnyTest);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("======= Find First ===========");
String findFirstTest = strList1.stream().filter(s -> s.contains("Alp")).findFirst().get();
System.out.println("Find first value: "+findFirstTest);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("======= All Match ===========");
boolean allMatch = strList1.stream().allMatch(s -> s.equalsIgnoreCase("Alp"));
System.out.println("All Match : "+allMatch);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("======= Any Match ===========");
boolean anyMatch = strList1.stream().anyMatch(s -> s.equalsIgnoreCase("Alp"));
System.out.println("Any Match : "+anyMatch);
System.out.println();
Complete Code:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Optional;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
class Student {
String studentName;
List<String> studentSubjects;
int salary;
/**
* @return the salary
*/
public int getSalary() {
return salary;
}
/**
* @param salary the salary to set
*/
public void setSalary(int salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
public String getStudentName() {
return studentName;
}
public void setStudentName(String studentName) {
this.studentName = studentName;
}
public List<String> getStudentSubjects() {
return studentSubjects;
}
public void setStudentSubjects(List<String> studentSubjects) {
this.studentSubjects = studentSubjects;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [studentName=" + studentName + ", studentSubjects=" + studentSubjects + "]";
}
}
public class Operations {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> strList1 = Arrays.asList("Zebra","Alpha", "Beta", "Charlie", "Delta", "Alp", "Alphine", "Alphabet");
List<Integer> intList = Arrays.asList(10,35,44,32,1);
Student student1 = new Student();
student1.setStudentName("Alpha Student");
List<String> stud1Subj = new LinkedList<String>();
stud1Subj.add("Computers");
stud1Subj.add(" Information Technology");
student1.setStudentSubjects(stud1Subj);
student1.setSalary(10000);
Student student2 = new Student();
student2.setStudentName("Beta Student");
List<String> stud2Subj = new LinkedList<String>();
stud2Subj.add("Java");
stud2Subj.add(" Spring");
student2.setStudentSubjects(stud2Subj);
student2.setSalary(200000);
List<Student> studList = Arrays.asList(student1, student2);
System.out.println("==================== STUDLIST========================");
System.out.println(studList);
System.out.println();
List<List<String>> mapList = studList.stream().map(Student::getStudentSubjects).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println("========== Map in Stream ==========");
mapList.forEach(System.out::print);
System.out.println();
List<String> flatmapList = studList.stream().map(Student::getStudentSubjects).flatMap(Collection::stream).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println("========== FlatMap in Stream ==========");
flatmapList.forEach(System.out::print);
System.out.println();
List<String> distincts = strList1.stream().distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println("========== Distinct ==========");
distincts.forEach(x -> System.out.print(x+" "));
System.out.println();
List<String> limits = strList1.stream().limit(3).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println("========== LIMIT ==========");
limits.forEach(x -> System.out.print(x+" "));
System.out.println();
Set<String> peekValue = strList1.stream().filter(x -> x.equals("Alpha")).peek(s -> System.out.println(s)).collect(Collectors.toSet());
System.out.println("========== PEEK ==========");
peekValue.forEach(x -> System.out.print(x+" "));
System.out.println();
List<String> skipList = strList1.stream().skip(3).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println("========== Skip ==========");
skipList.forEach(x -> System.out.print(x+" "));
System.out.println();
List<String> sorting = strList1.stream().sorted(Comparator.reverseOrder()).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println("========== Sorted Reverse ==========");
sorting.forEach(x -> System.out.print(x+" "));
System.out.println();
List<String> sorting1 = strList1.stream().sorted(Comparator.naturalOrder()).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println("========== Sorted Natural Order ==========");
sorting1.forEach(x -> System.out.print(x+" "));
System.out.println();
List<String> sorting2 = strList1.stream().sorted().collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println("========== SORTING ==========");
sorting2.forEach(x -> System.out.print(x+" "));
System.out.println();
long num = strList1.stream().count();
System.out.println("========== Count ==========");
System.out.println(num);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("==========min and max================");
int max = intList.stream().max(Integer::compare).get();
System.out.println("Max value is: "+max);
int min = intList.parallelStream().min(Integer::compare).get();
System.out.println("Min value is: "+min);
int min1 = intList.parallelStream().max(Comparator.reverseOrder()).get();
System.out.println("Min value 1 is: "+min1);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("======= for each ===========");
strList1.parallelStream().forEach(x -> System.out.print(x+" "));
System.out.println();
System.out.println("======= for each Ordering===========");
strList1.parallelStream().forEachOrdered(x -> System.out.print(x+" "));
System.out.println();
int reduce = intList.parallelStream().reduce((x1,x2)-> x1+x2).get();
System.out.println("======= Reduce ===========");
System.out.println("Reduce is: "+reduce);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("===========for each vs stream.foreach============");
strList1.forEach(s -> System.out.print(s+" "));
System.out.println();
strList1.parallelStream().forEach(s -> System.out.print(s+" "));
System.out.println();
//Filter operation
System.out.println("======= Filter ===========");
Optional<String> filterValue = strList1.parallelStream().filter(x -> x.equalsIgnoreCase("delta")).findFirst();
System.out.println("Filter with findfirst: "+filterValue);
System.out.println();
//Stream with Filter
String filterContains = strList1.stream().filter(s -> s.equalsIgnoreCase("charlie")).findAny().get();
System.out.println("Filter with findAny: "+filterContains);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("======= Find Any ===========");
boolean findAny = strList1.stream().filter(s -> s.equalsIgnoreCase("che")).findAny().isPresent();
System.out.println("FindAny isPresent: "+findAny);
System.out.println();
String findAnyTest = strList1.stream().filter(s -> s.contains("Alp")).findAny().get();
System.out.println("Find Any with value: "+findAnyTest);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("======= Find First ===========");
String findFirstTest = strList1.stream().filter(s -> s.contains("Alp")).findFirst().get();
System.out.println("Find first value: "+findFirstTest);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("======= All Match ===========");
boolean allMatch = strList1.stream().allMatch(s -> s.equalsIgnoreCase("Alp"));
System.out.println("All Match : "+allMatch);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("======= Any Match ===========");
boolean anyMatch = strList1.stream().anyMatch(s -> s.equalsIgnoreCase("Alp"));
System.out.println("Any Match : "+anyMatch);
System.out.println();
}
}