@Embeddable and @Embedded Annotation – Hibernate
We have seen some basic annotations of hibernate (here), Now we are going to see about @Embeddable and @Embedded annotations.
One entity can be embedded into another entity, One entity attributes may be common to more than one entity.
Let us understand with an example,
Consider we have 2 pojo’s – employee and manager. We create another pojo named address. Here address attribute is common for both employee and manager. Address has common attributes that are required by both these java classes. @Embeddable and @Embedded annotations play a major role in embedding address into employee and manager entities.
Lets see @Embeddable and @Embedded example for employee entity.
address.java
package com.javainfinite.pojo;
import javax.persistence.Embeddable;
@Embeddable
public class address {
private String state;
private String city;
private String pincode;
public String getState() {
return state;
}
public void setState(String state) {
this.state = state;
}
public String getCity() {
return city;
}
public void setCity(String city) {
this.city = city;
}
public String getPincode() {
return pincode;
}
public void setPincode(String pincode) {
this.pincode = pincode;
}
}
employee.java
package com.javainfinite.pojo;
import java.io.Serializable;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Embedded;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table (name="Employee")
public class employee implements Serializable {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
@Column(name="Employee_ID")
private int eid;
@Column(name="Employee_Name")
private String ename;
@Column(name="Employee_Password")
private String epass;
@Embedded
private address address1;
public address getAddress1() {
return address1;
}
public void setAddress1(address address1) {
this.address1 = address1;
}
public int getEid() {
return eid;
}
public void setEid(int eid) {
this.eid = eid;
}
public String getEname() {
return ename;
}
public void setEname(String ename) {
this.ename = ename;
}
public String getEpass() {
return epass;
}
public void setEpass(String epass) {
this.epass = epass;
}
}
NewHibernateUtil.java
package com.javainfinite.pojo;
import org.hibernate.cfg.AnnotationConfiguration;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
public class NewHibernateUtil {
private static final SessionFactory sessionFactory;
static {
try {
// Create the SessionFactory from standard (hibernate.cfg.xml)
// config file.
sessionFactory = new AnnotationConfiguration().configure().buildSessionFactory();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
// Log the exception.
System.err.println("Initial SessionFactory creation failed." + ex);
throw new ExceptionInInitializerError(ex);
}
}
public static SessionFactory getSessionFactory() {
return sessionFactory;
}
}
hibernate.cfg.xml
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<property name="hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto">update</property>
<property name="hibernate.dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.url">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/hibernateannotation</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.username">root</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.password">root</property>
<property name="hibernate.show_sql">true</property>
<mapping class="com.javainfinite.pojo.employee"/>
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration>
package com.javainfinite.exec;
import com.javainfinite.pojo.NewHibernateUtil;
import com.javainfinite.pojo.address;
import com.javainfinite.pojo.employee;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.Transaction;
public class Execution {
public static void main(String args[])
{
Session session=NewHibernateUtil.getSessionFactory().openSession();
try
{
Transaction transaction=session.beginTransaction();
employee emp=new employee();
address addr=new address();
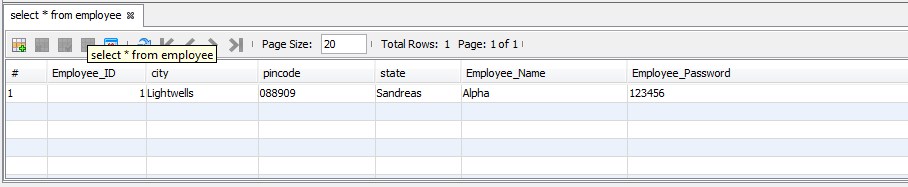
addr.setCity("Lightwells");
addr.setState("Sandreas");
addr.setPincode("088909");
emp.setEname("Alpha");
emp.setEpass("123456");
emp.setAddress1(addr);
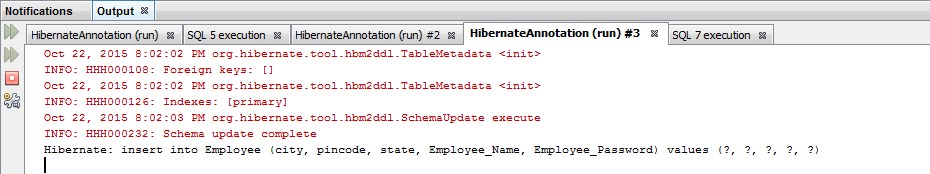
session.save(emp);
transaction.commit();
session.close();
}
catch(Exception e)
{
}
}
}
Note:
If you like to change the column name of address.java, use the same annotations of employee.java – @Column (name=””)

[…] Annotations In our previous example we had seen how to inject one entity into another entity(here). We have injected the address class into employee class. In that example we have not renamed the […]